1.两数求和:哈希映射
使用hashmap来实现,key里放要判别的数,value里放下标
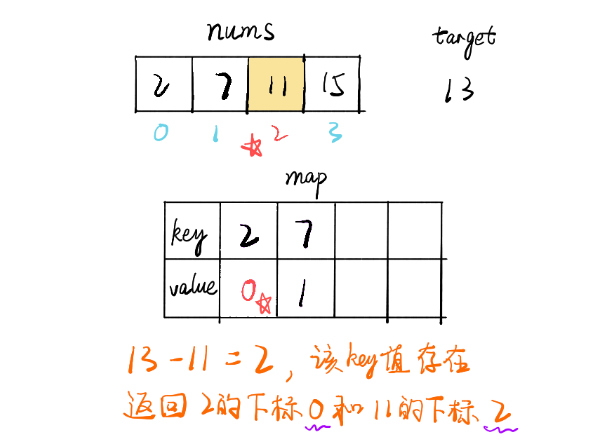
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(map.containsKey(target-nums[i])){
return new int[] {map.get(target-nums[i]),i};
}
map.put(nums[i],i);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution");
}
}
2.判断子序列:双指针
使用上下双指针,charAt()方法
class Solution {
public boolean isSubsequence(String s, String t) {
if(s.length()==0){
return true;
}
for(int i=0,j=0;j<t.length();j++){
if(s.charAt(i)==t.charAt(j)){
i++;
if(i==s.length()){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
3.回文数:字符串反转(慢) 双指针(略慢) 数字处理/%(快)
要先排除负数,121是回文数
字符串反转:
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
if(x<0){
return false;
}
StringBuilder zheng = new StringBuilder(x+"");
StringBuilder fan=new StringBuilder(zheng).reverse();//注意
if(zheng.toString().equals(fan.toString())){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
}
//优化(别人写的比我简洁多了)
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
if(x<0) return false;
String s = x + "";
StringBuilder n = new StringBuilder(s);
return n.reverse().toString().equals(s);
}
}
双指针:
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
String str=x+"";
int left=0;
int right=str.length()-1;
while(left<right){
if(str.charAt(left)==str.charAt(right)){
left++;
right--;
}else{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
数字处理:
class Solution {//自己真想不到吧
public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
if(x < 0)
return false;
int cur = 0;
int num = x;
while(num != 0) {
cur = cur * 10 + num % 10;
num /= 10;
}
return cur == x;
}
}
4.加一:数学解题%
题目:


//写出这个代码的人简直就是天才,我五体投地了。太特么聪明了
class Solution {
public int[] plusOne(int[] digits) {
for (int i = digits.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
digits[i]++;
digits[i] = digits[i] % 10;
if (digits[i] != 0) return digits;
}
digits = new int[digits.length + 1];
digits[0] = 1;
return digits;
}
}
5.爬楼梯:斐波那契数列(递归+hashmap,循环)
题目:

思路:其实就是斐波那契数列,比如一共n层,若第一步走1层,f(n-1)为后面n-1层的所有方法数,若第一步走2层,f(n-2)
为后面n-2层方法数,以此类推递归,直到后面只剩1层就只有1种方法了,只剩两层就只有2种方法了
但是直接递归大概率会超时,我们需要借助hashmap存储我们算过的f(n)防止重复计算
当然所有递归都可以改用循环代替
单纯递归(超时了):
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n==1) return 1;
if(n==2) return 2;
return climbStairs(n-1)+climbStairs(n-2);;
}
}
递归+hashmap:
class Solution {
private HashMap<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n==1) return 1;
if(n==2) return 2;
if(map.containsKey(n)){
return map.get(n);
}
int result = climbStairs(n-1)+climbStairs(n-2);
map.put(n,result);
return result;
}
}
循环:
class Solution {//纯纯斐波那契数列啊:1+2+3+5+8+...
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if(n==1) return 1;
if(n==2) return 2;
int start=1;
int end=2;
int result=0;
for(int i=2;i<n;i++){
result = start+end;
start=end;
end=result;
}
return result;
}
}
6.合并两个有序数组:双指针
题目:

解题:
sort()方法,直接拼接两个数组然后使用Arrays.sort():
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
nums1[m+i]=nums2[i];
}
Arrays.sort(nums1);
}
}
双指针(头):
//注意点:如果数组1或2提前全部排序完了,那就直接把剩下的另一个数组的数字依次加到后面就行
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int pt1=0;
int pt2=0;
int i=0;
int[] result=new int[m+n];
while(pt1<m || pt2<n){
if(pt1>=m && pt2<n){
result[i]=nums2[pt2++];
i++;
continue;
}
if(pt1<m && pt2>=n){
result[i]=nums1[pt1++];
i++;
continue;
}
if(nums1[pt1]<nums2[pt2]){
result[i]=nums1[pt1++];
i++;
}else{
result[i]=nums2[pt2++];
i++;
}
}
for(int j=0;j<m+n;j++){
nums1[j]=result[j];
}
}
}
//这个方法弊端就是需要额外创建一个数组,最后还要从新把数组赋值给nums1,于是有了下面的这种双指针方法(从尾部往前判断)
双指针(尾):
class Solution {//虽然但是,我自己写的时候都懵懵的,还是上面那种好写一点,这种方法空间复杂度好像也没少多少
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int pr1=m-1;
int pr2=n-1;
int index=m+n-1;
while(index>=0){
if(pr1<0){
nums1[index--]=nums2[pr2--];
continue;
}
if(pr2<0){
break;
}
if(nums1[pr1]>nums2[pr2]){
nums1[index--]=nums1[pr1--];
}else{
nums1[index--]=nums2[pr2--];
}
}
}
}
7.移动零:双指针
题目:
解题:
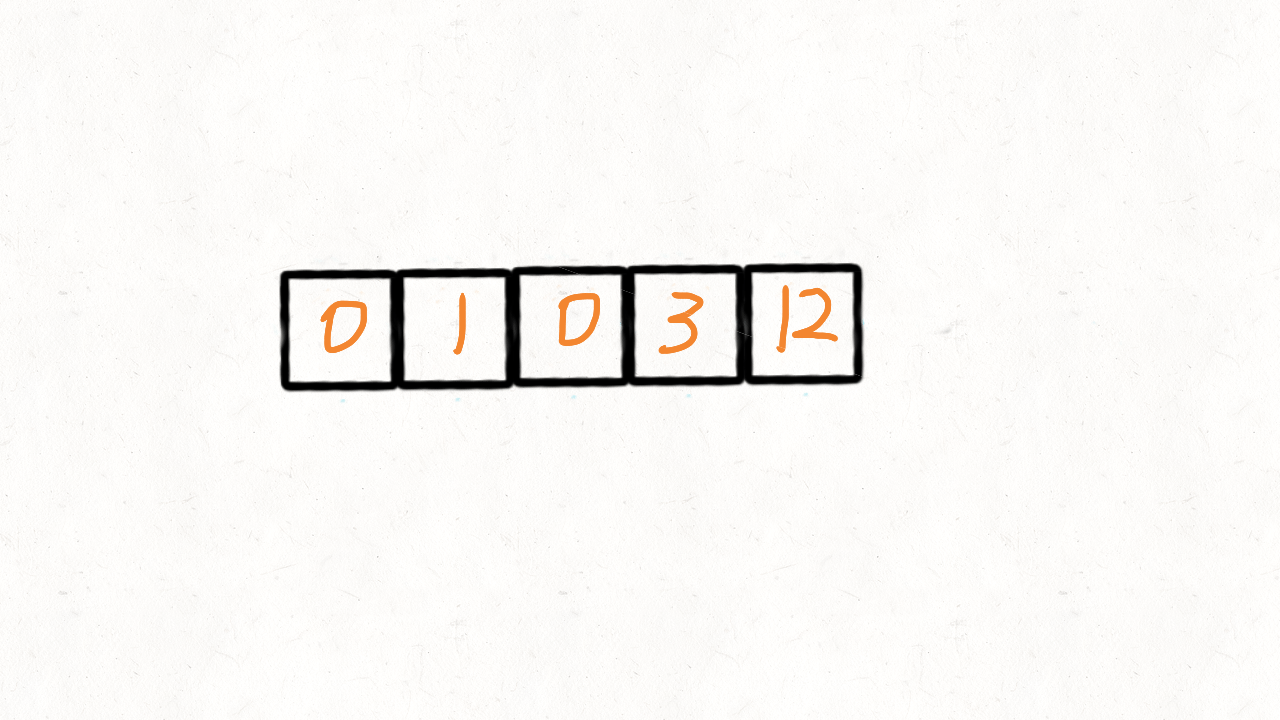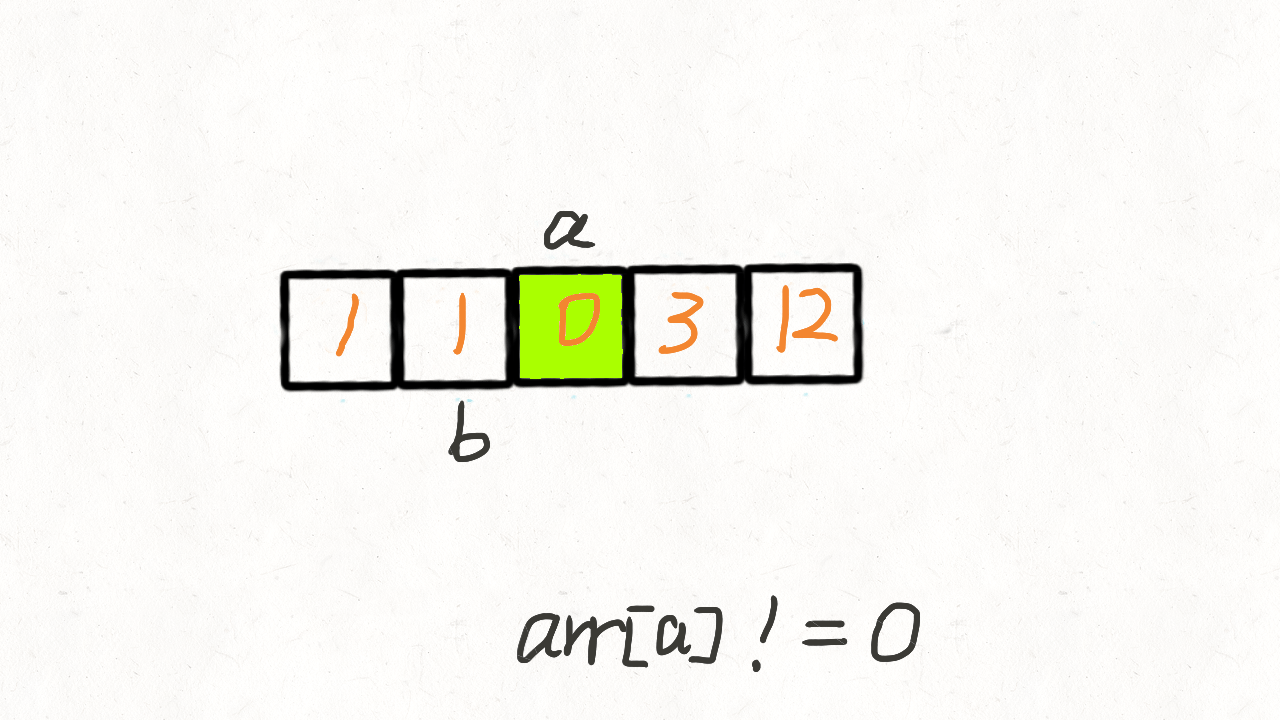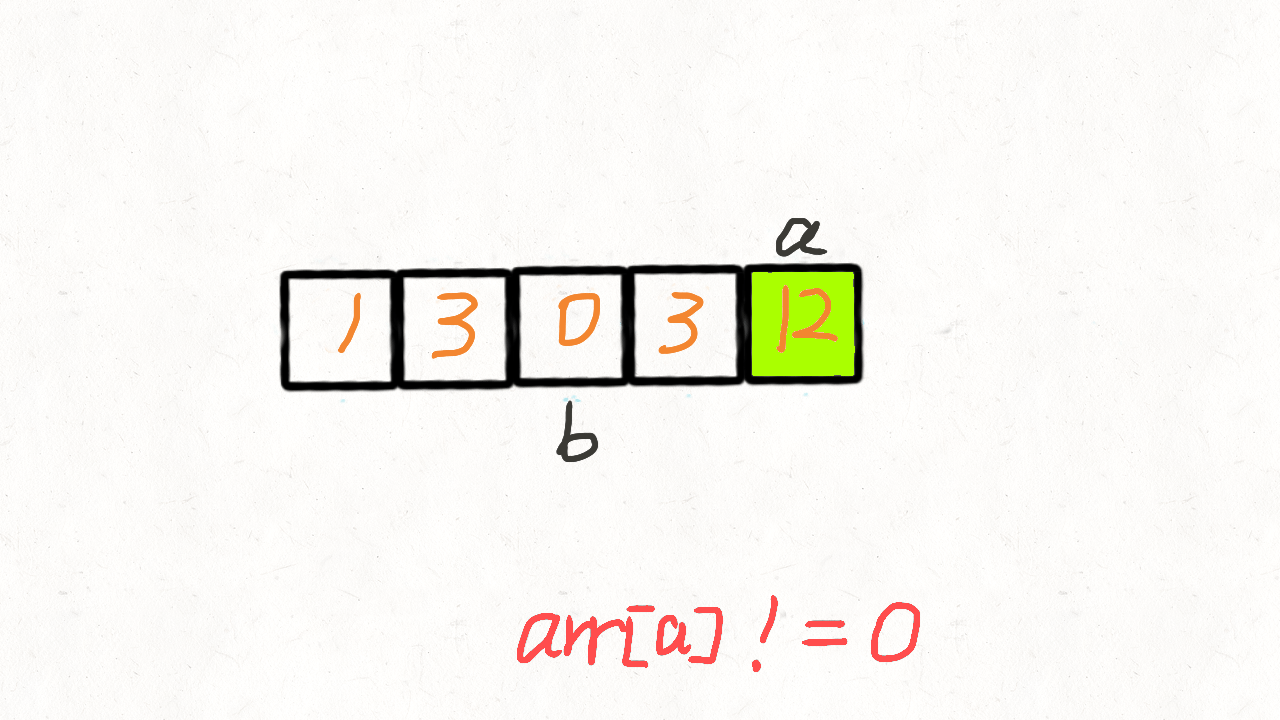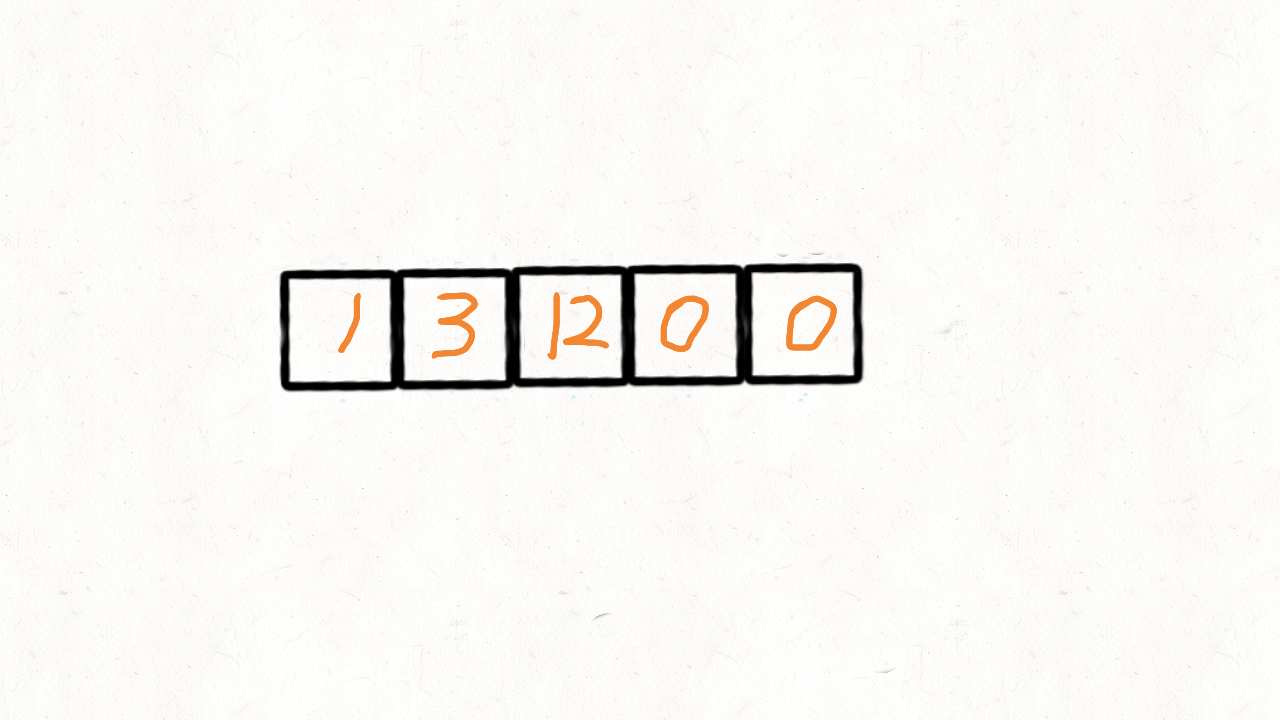
双指针:
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int j=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i]!=0){
nums[j++]=nums[i];
}
}
for(int i=j;i<nums.length;i++){
nums[i]=0;
}
}
}
8.找到所有数组中消失的数字:
要求:不使用额外空间,时间复杂度O(n)
题目:
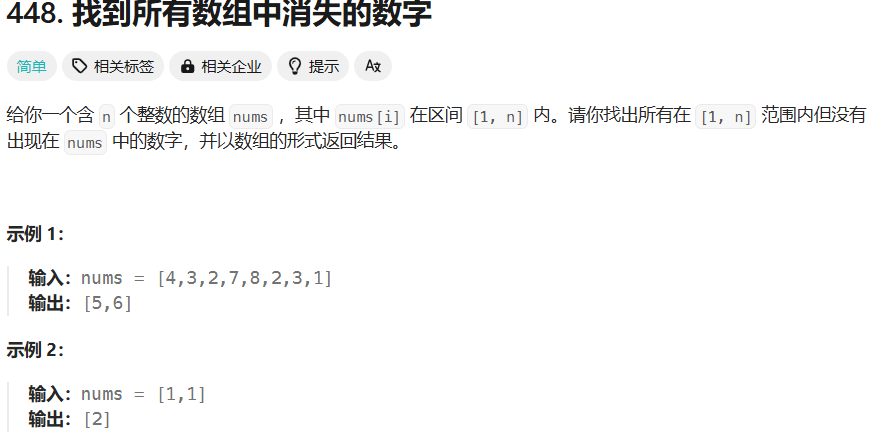
解题:
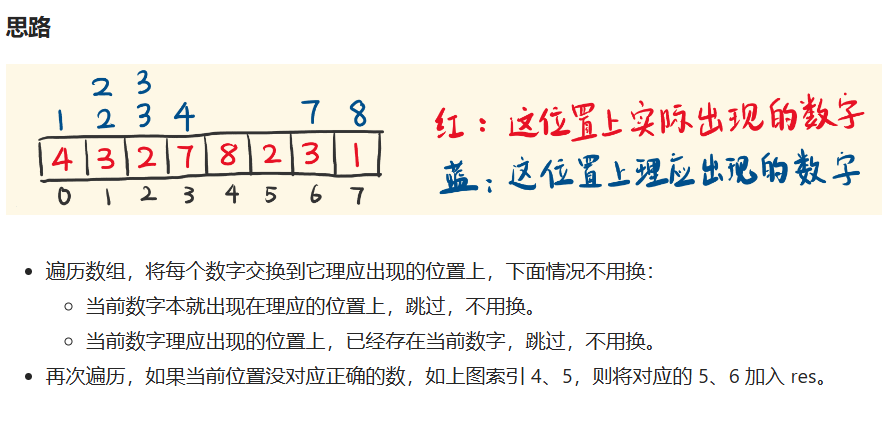
将数组放到他理应在的位置上:
class Solution {//看不明白,太难了这题,到最后都没明白
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0;
while (i < nums.length) {
if (nums[i] == i + 1) {
i++;
continue;
}
int idealIdx = nums[i] - 1;
if (nums[i] == nums[idealIdx]) {
i++;
continue;
}
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[idealIdx];
nums[idealIdx] = tmp;
}
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[j] != j + 1) {
res.add(j + 1);
}
}
return res;
}
}
最快答案:(也没看懂)
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
List<Integer> res = new LinkedList<>();
int n = nums.length;
for(int num: nums){
nums[(num -1)%n] += n;
}
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
//少的数在角标中找加一
if(nums[i] <= n)res.add(i+1);
}
return res;
}
}
9.合并两有序链表:双指针,递归
双指针:
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null) return list2;
if(list2==null) return list1;
ListNode result=new ListNode(0);
ListNode p=result;
while(list1!=null && list2!=null){
if(list1.val>list2.val){
p.next=list2;
list2=list2.next;
}else{
p.next=list1;
list1=list1.next;
}
p=p.next;
}
if(list1==null){
p.next=list2;
}
if(list2==null){
p.next=list1;
}
return result.next;
}
}
递归:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
//就是将大问题分为相同的小问题,就使用递归
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
if(list1==null) return list2;
if(list2==null) return list1;
if(list1.val>list2.val){
list2.next=mergeTwoLists(list1,list2.next);
return list2;
}else{
list1.next=mergeTwoLists(list1.next,list2);
return list1;
}
}
}
10.删除排序链表中的重复元素:正常遍历和递归
太简单了
解题:
正常遍历:
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return head;
}
if(head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode currentNode=head;
while(currentNode.next!=null){
if(currentNode.next.val==currentNode.val){
currentNode.next=currentNode.next.next;
}else{
currentNode=currentNode.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
递归:
大问题可以分成很多相同的小问题解决
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return head;
}
if(head.next==null){
return head;
}
if(head.next.val==head.val){
head.next=deleteDuplicates(head.next);
return head.next;
}
else{
head.next=deleteDuplicates(head.next);
return head;
}
}
}
11.环形链表:快慢指针
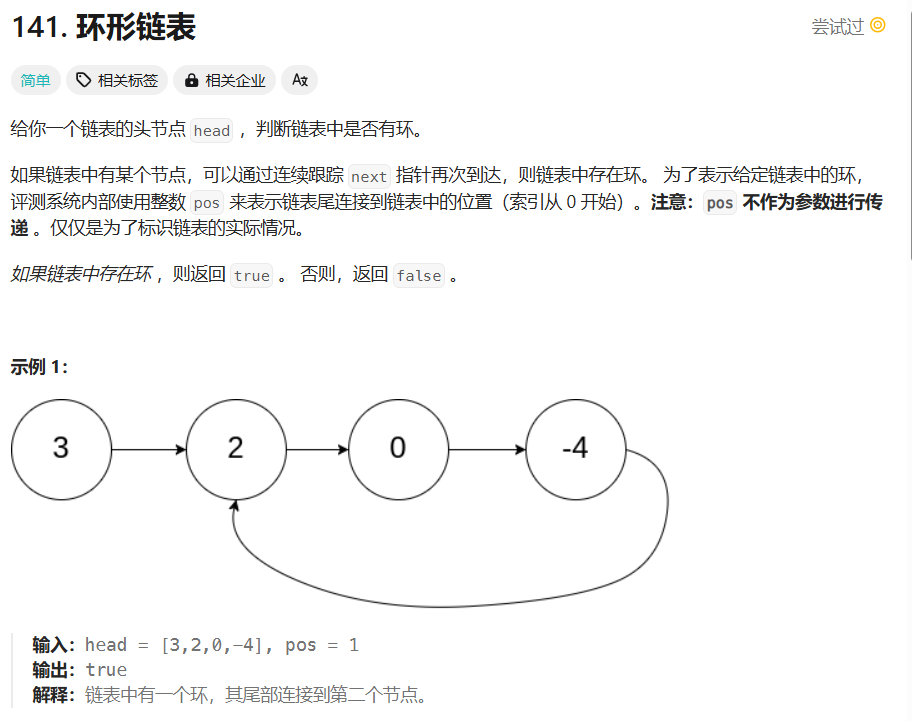
解题:
思路:快指针一次2步,慢指针一次1步
若有环路,快指针肯定会追上慢指针重合,若无环路,则快指针会到链表末尾null
快慢指针:
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null) return false;
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast.next!=null && fast.next.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast==slow){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
12.环形链表2 :快慢指针
环形链表的进阶,不仅要判断链表是否有环,有环时还要返回从哪个节点开始有环的
解题思路:
前面判断有环和原本快慢指针一样,当快慢指针指到一起时判断为有环,然后将慢指针放到链表头部,快指针不动但变为和慢指针一样的速度,然后同时往后移动,当两个指针再次相遇时的节点就是环入口节点。
先快慢指针,后速度一致:
public class Solution {
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
if(head==null || head.next==null){
return null;
}
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
boolean isCycle=false;
while(fast.next!=null && fast.next.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
if(fast==slow){
isCycle=true;
break;
}
}
if(isCycle==true){
slow=head;
while(slow!=fast){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
return null;
}
}
13.相交链表:双指针交错遍历
题目:
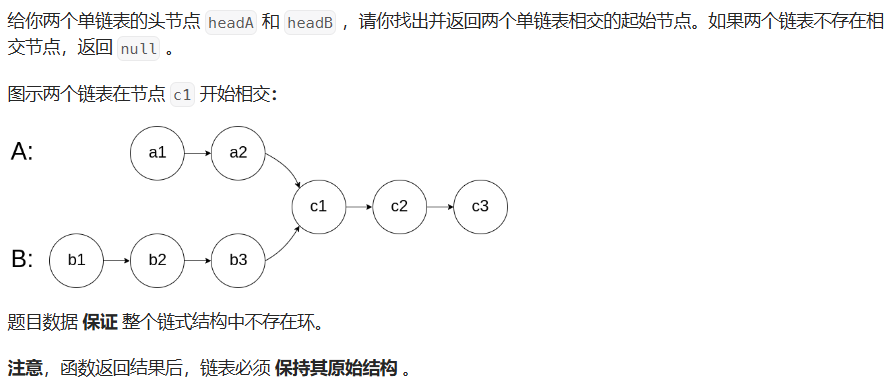
思路:
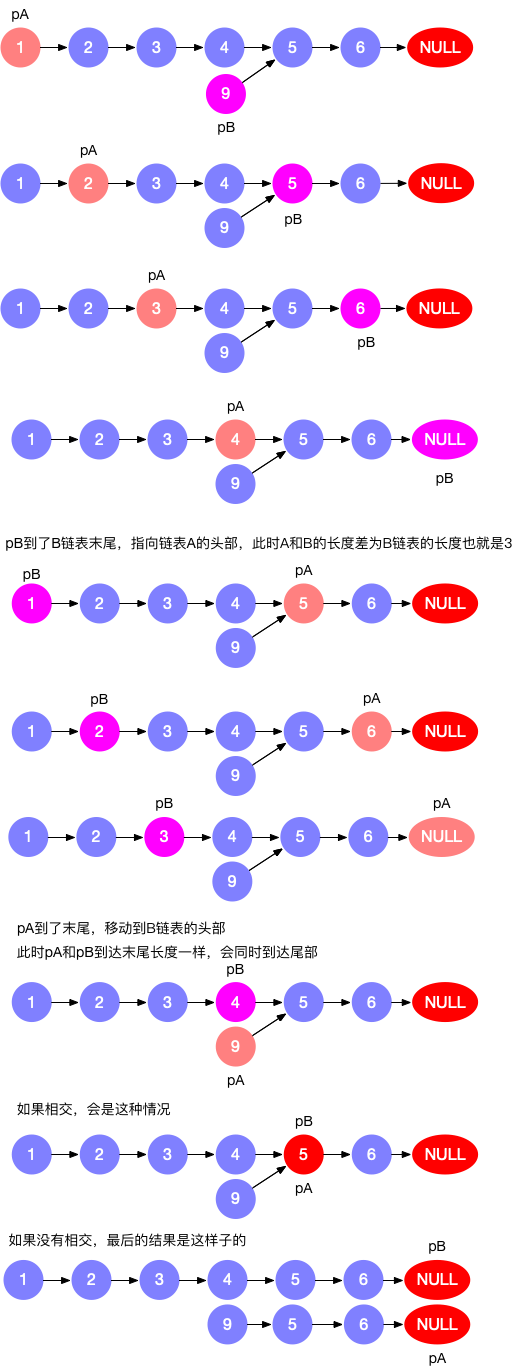
解题:
双指针交错遍历:
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if(headA==null) return null;
if(headB==null) return null;
ListNode p1=headA;
ListNode p2=headB;
while(p1!=p2){
p1=(p1==null?headB:p1.next);
p2=(p2==null?headA:p2.next);
}
return p1;
}
}
14.反转链表:双指针
两个指针,per指向当前节点前一个节点(初始为null) cur节点指向当前节点 ,同时每次遍历前都要记录当前节点的下一个节点
双指针:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre= null;
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode nextNode=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=nextNode;
}
return pre;
}
}
15.回文链表:快慢指针+反转链表
思路:
快慢指针来遍历,快指针遍历到尾巴后,慢指针正好在链表中间,分奇数偶数情况,偶数的话快指针最后为null,奇数的话快指针最后的next为null,以此来区分奇数偶数,如果为奇数,慢指针还需要向后挪一位,然后反转慢指针后面的一段链表,快指针再重新指向整个链表头部,然后快慢指针同速度往下比较,若有不同则表示不是回文链表,慢指针为null时结束
快慢指针+反转链表:
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if(head==null) return false;
if(head.next==null) return true;
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next.next;
}
if(fast!=null){
slow=slow.next;
}
fast=head;
slow=reserveNode(slow);
while(slow!=null){
if(slow.val!=fast.val){
return false;
}
slow=slow.next;
fast=fast.next;
}
return true;
}
public ListNode reserveNode(ListNode head) {
if(head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode per=null;
ListNode cur=head;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode nextNode=cur.next;
cur.next=per;
per=cur;
cur=nextNode;
}
return per;
}
}
16.链表的中间节点:快慢指针
快慢指针:
class Solution {
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
if(head==null) return null;
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
fast=fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
17.链表中倒数第k个节点:双指针 前后指针
思路:
前面的指针先往后移k-1位,然后前后指针同时往后一步一步移动,前指针为null时,后指针所指向的节点就是倒数第k个节点
双指针 前后指针:
class Solution {
public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode fast=head;
ListNode slow=head;
while(k-1>=0){
k--;
fast=fast.next;
}
while(fast!=null){
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow.val;
}
}
18.找出与数组相加的整数1:最小值之差
题目:

思路:
拿到nums1和nums2的最小值,之差就是答案
最小值之差:
class Solution {
public int addedInteger(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int n1=min(nums1);
int n2=min(nums2);
return n2-n1;
}
private int min(int[] nums){
int res=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for(int num : nums){
res=Math.min(res,num);
}
return res;
}
}
19.用栈模拟队列:两个栈
题目:

思路:
push到第一个栈中,pop是从第二个栈中pop,如果第二个栈为空就把第一个栈的元素pop出来push到第二个栈再pop出来,先进后出+先进后出=先进先出
两个栈:
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> A;
private Stack<Integer> B;
public MyQueue() {
A=new Stack<>();
B=new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
A.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(B.isEmpty()){
while(!A.isEmpty()){
B.push(A.pop());
}
}
return B.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(B.isEmpty()){
while(!A.isEmpty()){
B.push(A.pop());
}
}
return B.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
if(A.isEmpty() && B.isEmpty()){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
20.字符串解码:栈
题目:

地址:
答案:
栈:
class Solution {
int ptr;
public String decodeString(String s) {
LinkedList<String> stk = new LinkedList<String>();
ptr = 0;
while (ptr < s.length()) {
char cur = s.charAt(ptr);
if (Character.isDigit(cur)) {
// 获取一个数字并进栈
String digits = getDigits(s);
stk.addLast(digits);
} else if (Character.isLetter(cur) || cur == '[') {
// 获取一个字母并进栈
stk.addLast(String.valueOf(s.charAt(ptr++)));
} else {
++ptr;
LinkedList<String> sub = new LinkedList<String>();
while (!"[".equals(stk.peekLast())) {
sub.addLast(stk.removeLast());
}
Collections.reverse(sub);
// 左括号出栈
stk.removeLast();
// 此时栈顶为当前 sub 对应的字符串应该出现的次数
int repTime = Integer.parseInt(stk.removeLast());
StringBuffer t = new StringBuffer();
String o = getString(sub);
// 构造字符串
while (repTime-- > 0) {
t.append(o);
}
// 将构造好的字符串入栈
stk.addLast(t.toString());
}
}
return getString(stk);
}
public String getDigits(String s) {
StringBuffer ret = new StringBuffer();
while (Character.isDigit(s.charAt(ptr))) {
ret.append(s.charAt(ptr++));
}
return ret.toString();
}
public String getString(LinkedList<String> v) {
StringBuffer ret = new StringBuffer();
for (String s : v) {
ret.append(s);
}
return ret.toString();
}
}
21.二叉树中序遍历:递归
题目:
中序遍历:
class Solution {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return list;
}
doTree(root);
return list;
}
private void doTree(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return;
}
doTree(node.left);
list.add(node.val);
doTree(node.right);
}
}
22.二叉树前序遍历:递归
class Solution {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return list;
}
doTree(root);
return list;
}
private void doTree(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return;
}
list.add(node.val);
doTree(node.left);
doTree(node.right);
}
}
23.二叉树后序遍历:递归
class Solution {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null){
return list;
}
doTree(root);
return list;
}
private void doTree(TreeNode node){
if(node==null){
return;
}
doTree(node.left);
doTree(node.right);
list.add(node.val);
}
}
24.对称二叉树:递归
思路:
递归比较左节点的左节点和右节点的右节点是否相同,左节点的右节点和右节点的左节点是否相同,递归结束条件是看比较的两个节点都为null返回true,有一个为null那肯定不对称,若值不相等也不对称,以上都不满足则递归第一句的比较。
递归:
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return false;
return deepTree(root.left,root.right);
}
private boolean deepTree(TreeNode left,TreeNode right){
if(left==null && right==null){
return true;
}
//若只有一个等于null,则必不对称
if(left==null || right==null){
return false;
}
if(left.val!=right.val){
return false;
}
return deepTree(left.left,right.right) && deepTree(left.right,right.left);
}
}
25.二叉树的最大深度:递归
递归:
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return 0;
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left),maxDepth(root.right))+1;
}
}
26.平衡二叉树:递归+最大深度
高度平衡二叉树定义:一个二叉树每个节点的左右两子树的高度差不能大于1
思路:
其实就是在最大深度的题目代码上改造,递归判断左右子树最大高数之差是否大于1,但凡中途有一个子树不是平衡二叉树,那么整棵树肯定不是平衡二叉树了,返回-1
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return true;
return balanceTree(root)!=-1;
}
private int balanceTree(TreeNode node){
if(node==null) return 0;
int left=balanceTree(node.left);
int right=balanceTree(node.right);
if(left==-1 || right==-1 || Math.abs(left-right)>1){
return -1;
}
return Math.max(left,right)+1;
}
}
27.翻转二叉树:递归
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return null;
invertTree(root.left);
invertTree(root.right);
TreeNode temp=root.left;
root.left=root.right;
root.right=temp;
return root;
}
}
特别篇:十大排序算法
1.冒泡排序
2.选择排序
冒泡排序和选择排序差不多,选择排序相当于冒泡的优化,只有选到最大的数再交换,减少了交换的次数
平均时间复杂度:O(n^2)
空间复杂度: O(1)
3.插入排序
插入排序对于部分有序的数组十分高效,也很适合小规模数组
对于大规模的乱序数组很慢
平均时间复杂度:O(n^2)
空间复杂度: O(1)
4.快速排序
使用分治法将原始数据分为较小的子集,并递归地对这些子集进行排序;
优点:正常情况下非常高效,时间:O(n log n) 空间:O(log n)
缺点:当要排序的数组本身就有序或者逆序或存在大量重复元素的时候,可能导致分区后的子数组长度与原数组长度几乎相同,时间复杂度退化为 O(n^2)
5.希尔排序
基于插入排序 不稳定的排序算法
需要增量序列,没有指定最好的增量序列
希尔增量序列:{N/2,(N/2)/2......1}
Hibbard序列:{2^k-1,...,3,1}
6.归并排序
通过递归和分而治之实现
7.堆排序
8.计数排序
仅适用于待排序元素为整数,分布较连续,跨度小的情况
9.桶排序
10.基数排序
28.手撕快速排序:
刘梦杰自己写的:
public class QuickSort {
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr={10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};
int n=arr.length;
System.out.println("原数组:");
for(int num:arr){
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
quickSort(arr,0,n-1);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("排序后:");
for(int num:arr){
System.out.print(num+" ");
}
}
private static void quickSort(int[] arr,int left,int right){
if(left>=right) return;
//选数组最右边的作为基准点
int standPoint=arr[right];
//分类下标(把数组分成做左右部分的中间下标)
int index=left-1;
//遍历下标
int i=left;
//遍历
while (i<right){
if(arr[i]<=standPoint){
index++;
if (index<i){
int temp=arr[i];
arr[i]=arr[index];
arr[index]=temp;
}
}
i++;
}
index++;
int temp=arr[right];
arr[right]=arr[index];
arr[index]=temp;
quickSort(arr,left,index-1);
quickSort(arr,index+1,right);
}
}
网上的:
public class QuickSort {
// 主方法,用于测试快速排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {10, 7, 8, 9, 1, 5};
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println("Unsorted array: ");
printArray(arr);
quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1);
System.out.println("\nSorted array: ");
printArray(arr);
}
// 快速排序主方法
public static void quickSort(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
// 获取分区索引
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
// 对分区左侧和右侧分别进行快速排序
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
// 分区方法
public static int partition(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
int pivot = arr[high]; // 选择最右边的元素作为基准点
int i = (low - 1); // 记录小于基准点的元素的索引
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
// 如果当前元素小于或等于基准点
if (arr[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
// 交换 arr[i] 和 arr[j]
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
// 将基准点放到正确的位置上
int temp = arr[i + 1];
arr[i + 1] = arr[high];
arr[high] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
// 打印数组
public static void printArray(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
28.2 手撕归并排序:
class Solution {
public int[] sortArray(int[] nums) {
return sort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
private int[] sort(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (right - left + 1 < 2) return new int[]{nums[left]};//重点注意
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
return merge(sort(nums, left, mid), sort(nums, mid + 1, right));
}
private int[] merge(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int i = 0, j = 0, k = 0;
int[] result = new int[nums1.length + nums2.length];
while (k < result.length) {
if (i >= nums1.length) {
result[k++] = nums2[j++];
} else if (j >= nums2.length) {
result[k++] = nums1[i++];
} else if (nums1[i] <= nums2[j]) {
result[k++] = nums1[i++];
} else {
result[k++] = nums2[j++];
}
}
return result;
}
}
29.二分查找:循环,递归
二分查找前提条件是需要查找的数组是有序的
循环:
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int left=0;
int right=nums.length-1;
while(left<=right){
int mid=(left+right)/2;
if(nums[mid]>target){
right=mid-1;//注意:需要mid-1
}else if(nums[mid]<target){
left=mid+1;//注意:需要mid+1
}else if(nums[mid]==target){
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
递归:
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int left=0;
int right=nums.length-1;
return doSearch(left,right,nums,target);
}
private int doSearch(int left,int right,int[] nums,int target){
if(left>right){
return -1;
}
int mid=(left+right)/2;
if(nums[mid]>target){
return doSearch(left,mid-1,nums,target);
}else if(nums[mid]<target){
return doSearch(mid+1,right,nums,target);
}else{
return mid;
}
}
}
特别篇:原码反码补码和位运算
正数的原码反码补码都是一样的,
负数的反码为源码取反(符号位除外)
负数的补码为反码+1
位运算:
按位与 &
按位或 |
按位非 ~
按位异或 ^
有符号右移 >>(正数高位补0,负数高位补1)
有符号左移 <<
无符号右移 >>>(无论正负,高位都补0)
两数交换:
a=1,b=3
a=a+b;
b=a-b;
a=a-b;
a=1,b=3
a=a^b;
b=a^b;
a=a^b;
判断奇偶数:
a=4,b=5
a&1==0?"偶数":"奇数";
b&1==0?"偶数":"奇数";
30.只出现一次的数字:异或^
题目:
思路:
题目只有一个数字只出现一次,其他数字都只出现两次,就可以用^来解决,
因为同一个数异或自己就等于0,0异或一个数还是那个数本身,所以我们依次都异或一遍,最后得出的数就是
只出现一次的数
异或:
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int res=0;
for(int num:nums){
res=res^num;
}
return res;
}
}
31.比特位计数:位运算,N的二进制中1的个数=[N&(N-1)]这个数字1的个数+1
题目:
题解:
位运算,N的二进制中1的个数=[N&(N-1)]这个数字1的个数+1

很难懂:
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] nums=new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
nums[i]=nums[i&(i-1)]+1;
}
return nums;
}
}
利用奇偶数判断:
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] nums=new int[n+1];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
nums[i]= ((i&1)==1?nums[i-1]+1:nums[i>>1]);
}
return nums;
}
}
刘梦杰自己写,易懂一点:
class Solution {
public int[] countBits(int n) {
int[] nums=new int[n+1];
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
int count=0;
int j=i;
while(j!=0){
j=j&(j-1);
count++;
}
nums[i]=count;
}
return nums;
}
}
32.汉明距离:位运算异或^
题目:

思路:
结合31题:
异或:
class Solution {
public int hammingDistance(int x, int y) {
int xor=x^y;
int n=0;
while(xor!=0){
xor=xor&(xor-1);
n++;
}
return n;
}
}
33.有效的括号:栈

解题:
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack=new Stack<Character>();
char[] arr=s.toCharArray();
for(char a:arr){
if(a=='('){
stack.push(')');
}else if(a=='{'){
stack.push('}');
}else if(a=='['){
stack.push(']');
}else{
if(stack.isEmpty() || stack.pop()!=a){
return false;
}
}
}
if(!stack.isEmpty()) return false;
return true;
}
}
34.字符串相加:双指针
题目:

双指针:
class Solution {
public String addStrings(String num1, String num2) {
int t=0;
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder("");
for(int i=num1.length()-1,j=num2.length()-1;i>=0 || j>=0;i--,j--){
int n1=(i>=0)?num1.charAt(i)-'0':0;
int n2=(j>=0)?num2.charAt(j)-'0':0;
res.append((n1+n2+t)%10);
t=(n1+n2+t)/10;
}
if(t==1){
res.append(1);
}
return res.reverse().toString();
}
}
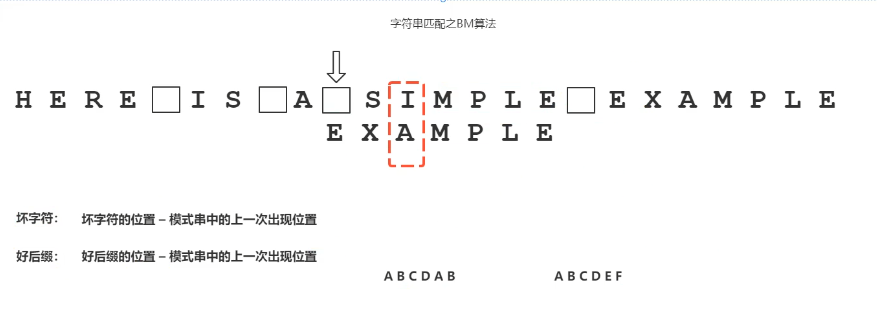
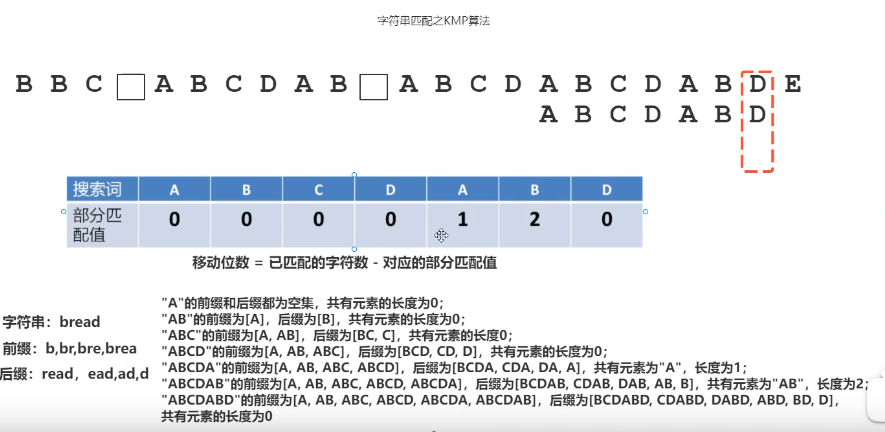
特别篇:字符串匹配BM算法和KMP算法
BM算法:
KPM算法:
35.最大子数组和:动态规划
题目:

解题:
动态规划(更清晰易懂):
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
//动态规划
int[] dp=new int[nums.length];
dp[0]=nums[0];
int max=nums[0];
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){
dp[i]=Math.max(nums[i],dp[i-1]+nums[i]);
if(max<dp[i]){
max=dp[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}
优化改良版动态规划:
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int cur = 0;
int result = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
cur += nums[i];
result = Math.max(cur,result);
if(cur < 0) cur = 0;
}
return result;
}
}
36.买卖股票的最佳时机:记录+遍历

思路:
每次都假设是今天卖出,然后求今天之前的历史最低点与今天的差价,记录最大差价。
记录+遍历:
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if(prices==null) return 0;
int maxProfit=0;
int minPrice=prices[0];
for(int i=0;i<prices.length;i++){
int todayProfit=prices[i]-minPrice;
if(todayProfit>maxProfit){
maxProfit=todayProfit;
}
if(minPrice>prices[i]){
minPrice=prices[i];
}
}
return maxProfit;
}
}
37.用 Rand7() 实现 Rand10():
题目:

思路:

代码:
class Solution extends SolBase {
public int rand10() {
int rand=(rand7()-1)*7+rand7();
while(rand>40){
rand=(rand7()-1)*7+rand7();
}
return rand%10+1;
}
}
38.搜索插入位置:二分查找
题目:

解题:
二分查找:
class Solution {
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
int left=0;
int right=nums.length-1;
while(left<=right){
int mid=(left+right)/2;
if(nums[mid]>target){
right=mid-1;
}else if(nums[mid]<target){
left=mid+1;
}else{
return mid;
}
}
return left;
}
}
39.杨辉三角
题目:
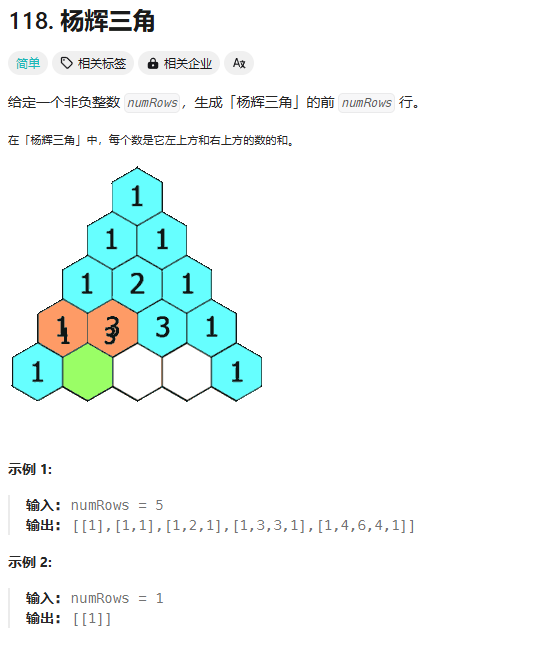
思路:

代码:
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> result=new ArrayList<List<Integer>>(numRows);
result.add(List.of(1));
for(int i=1;i<numRows;i++){
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>(i+1);
list.add(1);
for(int j=1;j<i;j++){
list.add(result.get(i-1).get(j-1)+result.get(i-1).get(j));
}
list.add(1);
result.add(list);
}
return result;
}
}
40.多数元素:摩尔投票
题目:
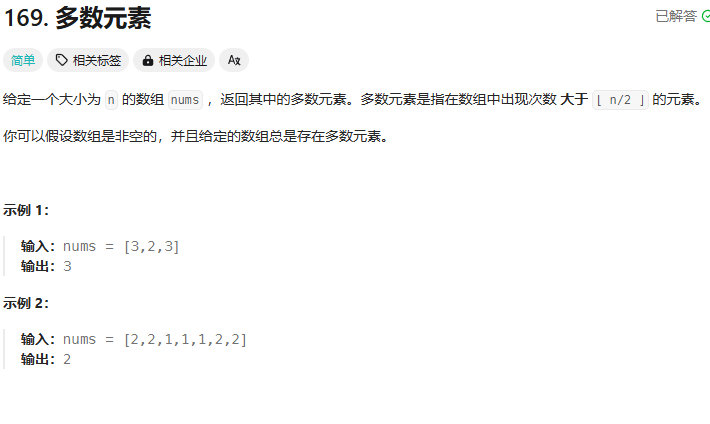
思路:
抵消原则
摩尔投票,设众数和票数
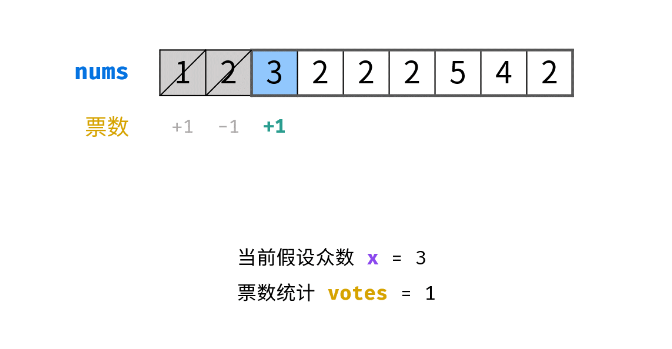
遍历数组,每当票数被抵消为0时设当前数字为众数,然后票数+1,往后遇到不同的数票数就-1,直到票数为0重新此步骤,最后留下来的众数就是多数元素
摩尔投票:
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int zz=nums[0];//众数
int count=0;//票数
for(int n:nums){
if(count==0){
zz=n;
}
if(n==zz){
count+=1;
}else{
count-=1;
}
}
return zz;
}
}
41.移除元素:双指针
题目:

思路:

双指针:
class Solution {
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int slow=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i]!=val){
nums[slow]=nums[i];
slow++;
}
}
return slow;
}
}
42.有序数组的平方:双指针
题目:

思路:

双指针:
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] nums) {
int left=0;
int right=nums.length-1;
int index=nums.length-1;
int[] res=new int[nums.length];
while(left<=right){
int l=nums[left]*nums[left];
int r=nums[right]*nums[right];
if(l>r){
left++;
res[index]=l;
index--;
}else{
right--;
res[index]=r;
index--;
}
}
return res;
}
}
43.长度最小的子数组:前后双指针(滑动窗口)
题目:

思路:

前后双指针代替队列:
class Solution {
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int left=0;
int right=0;
int min=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int sum=0;
while(right<nums.length){
sum+=nums[right++];
while(sum>=target){//把前面的数一个一个退出判断sum还大不大于target
min=Math.min(min,right-left);
sum-=nums[left];
left++;
}
}
return min == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : min;
}
}
44.特殊数组2
题目:

代码:
a[]数组存两个数字中间的逗号记录左右两边的数是否奇偶性一致,然后累加,最后判断两个下标的a是否相等,若相等则表示下标中的一段数字都是奇偶性不一致的,所以都是累加0,所以相等,所以返回true
class Solution {
public boolean[] isArraySpecial(int[] nums, int[][] queries) {
int[] a=new int[nums.length];
boolean[] ans=new boolean[queries.length];
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i]%2==nums[i-1]%2){
a[i]=a[i-1]+1;
}
else{
a[i]=a[i-1]+0;
}
}
for(int j=0;j<queries.length;j++){
ans[j]=a[queries[j][0]]==a[queries[j][1]];
}
return ans;
}
}
45.删除有序数组中的重复项:快慢指针
题目:

思路:
快指针元素等于慢指针元素,快指针后移,快指针元素不等于慢指针元素,慢指针先后移再覆盖为快指针元素,然后快指针后移
另一种说法:(慢指针相当于新数组的遍历,快指针来遍历原数组,只有当快指针元素没有重复时候,慢指针才会后移并写入未重复元素)
快慢指针:
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
int fast=0;
int slow=0;
while(fast<nums.length){
if(nums[fast]!=nums[slow]){
slow++;
nums[slow]=nums[fast];
}
fast++;
}
return slow+1;
}
}
46.将有序数组转换成二叉搜索数:递归
题目:
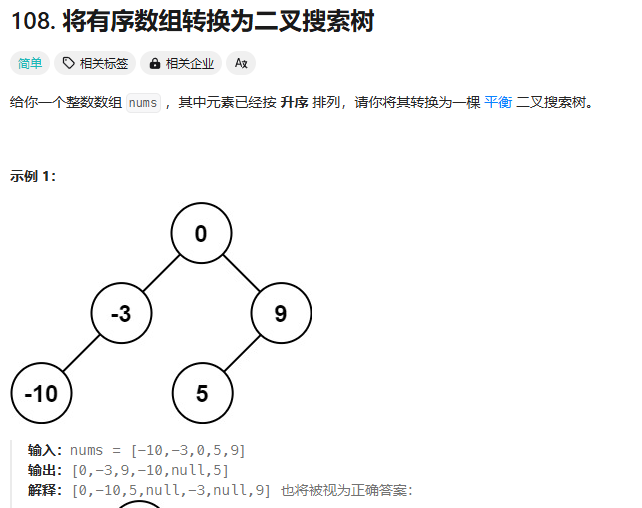
思路:
中序遍历,root选有序数组的最中间的元素,然后递归造左右子树
递归:
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
int left=0;
int right=nums.length-1;
return createTree(nums,left,right);
}
private TreeNode createTree(int[] nums,int left,int right){
if(left>right) return null;
int mid=(left+right)/2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left=createTree(nums,left,mid-1);
root.right=createTree(nums,mid+1,right);
return root;
}
}
47.无重复字符的最长子串:滑动窗口
题目:

思路:
其实就是一个队列,比如例题中的 abcabcbb,进入这个队列(窗口)为 abc 满足题目要求,当再进入 a,队列变成了 abca,这时候不满足要求。所以,我们要移动这个队列!
如何移动?
我们只要把队列的左边的元素移出就行了,直到满足题目要求!
滑动窗口:
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int max=0;
int left=0;
HashMap<Character,Integer> map=new HashMap<Character,Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++){
if(map.containsKey(s.charAt(i))){
left=Math.max(left,map.get(s.charAt(i)) + 1);
}
map.put(s.charAt(i),i);
max=Math.max(i-left+1,max);
}
return max;
}
}
48.二叉树的直径:递归
题目:
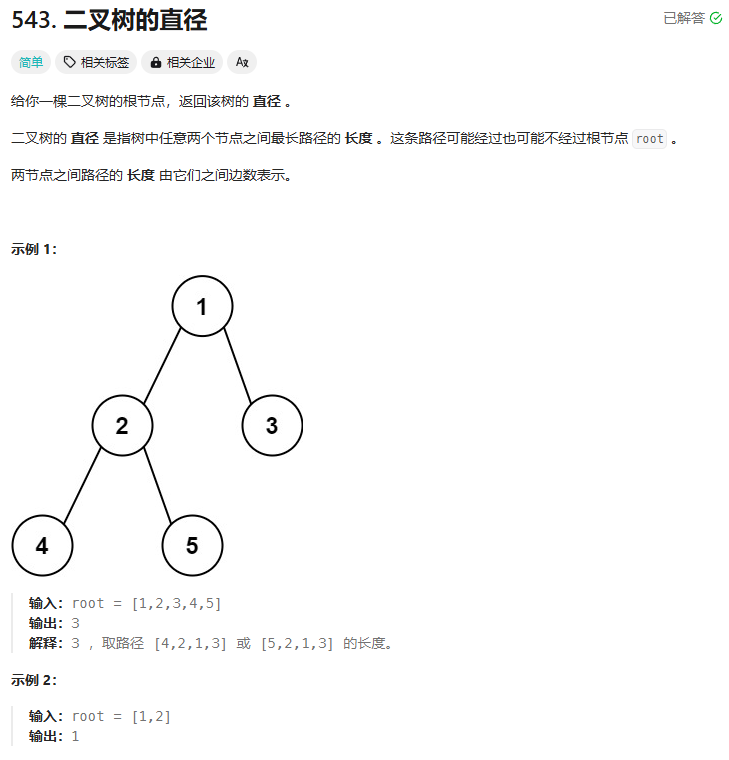
递归:
class Solution {
private int ans;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return -1;
}
int left=dfs(root.left)+1;
int right=dfs(root.right)+1;
ans=Math.max(ans,left+right);
return Math.max(left,right);
}
}
49.跳跃游戏:贪心算法
题目:

思路:
从头到尾遍历数组一遍,算出每个位置能到达的最远位置记录到max里,如果max大于数组最后一个下标则表示可以到达,如果中途遍历的i大于了最远到达长度表示卡在一个地方了不能到达最后一个下标
贪心算法:
//标准题解:
public class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int rightmost = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (i <= rightmost) {
rightmost = Math.max(rightmost, i + nums[i]);
if (rightmost >= n - 1) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
//刘梦杰题解:
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
int max=0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(i>max){
return false;
}
max=(max>i+nums[i]?max:i+nums[i]);
if(max>=nums.length-1){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
50.员工的重要性:哈希表+DFS

哈希表+DFS:
class Solution {
public int getImportance(List<Employee> employees, int id) {
Map<Integer, Employee> employeeMap = new HashMap<>(employees.size());
for (Employee e : employees) {
employeeMap.put(e.id, e);
}
return dfs(employeeMap, id);
}
private int dfs(Map<Integer, Employee> employeeMap, int id) {
Employee e = employeeMap.get(id);
int res = e.importance;
for (int subId : e.subordinates) {
res += dfs(employeeMap, subId);
}
return res;
}
}